Serverless computing has revolutionized the way developers build, deploy, and scale applications. With serverless computing, developers no longer need to manage servers, infrastructure, or the operating system. Instead, they can focus on writing code and building applications that are scalable, efficient, and cost-effective.
AWS Lambda and API Gateway are two of the most popular serverless computing services provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). In this blog, we will discuss the basics of serverless computing, AWS Lambda, and API Gateway, and how to use them to build a serverless web application.
Basics of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider manages the infrastructure and automatically allocates computing resources as needed. The key benefits of serverless computing are scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Lambda functions can be used to process data, respond to events, and more. AWS Lambda supports a wide range of programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, Go, and Ruby.
API Gateway
AWS API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, and manage RESTful APIs. It integrates with AWS Lambda, allowing developers to create serverless APIs that can be used to build scalable web applications. API Gateway provides features such as authentication, authorization, and rate limiting, making it a powerful tool for building secure and efficient APIs.
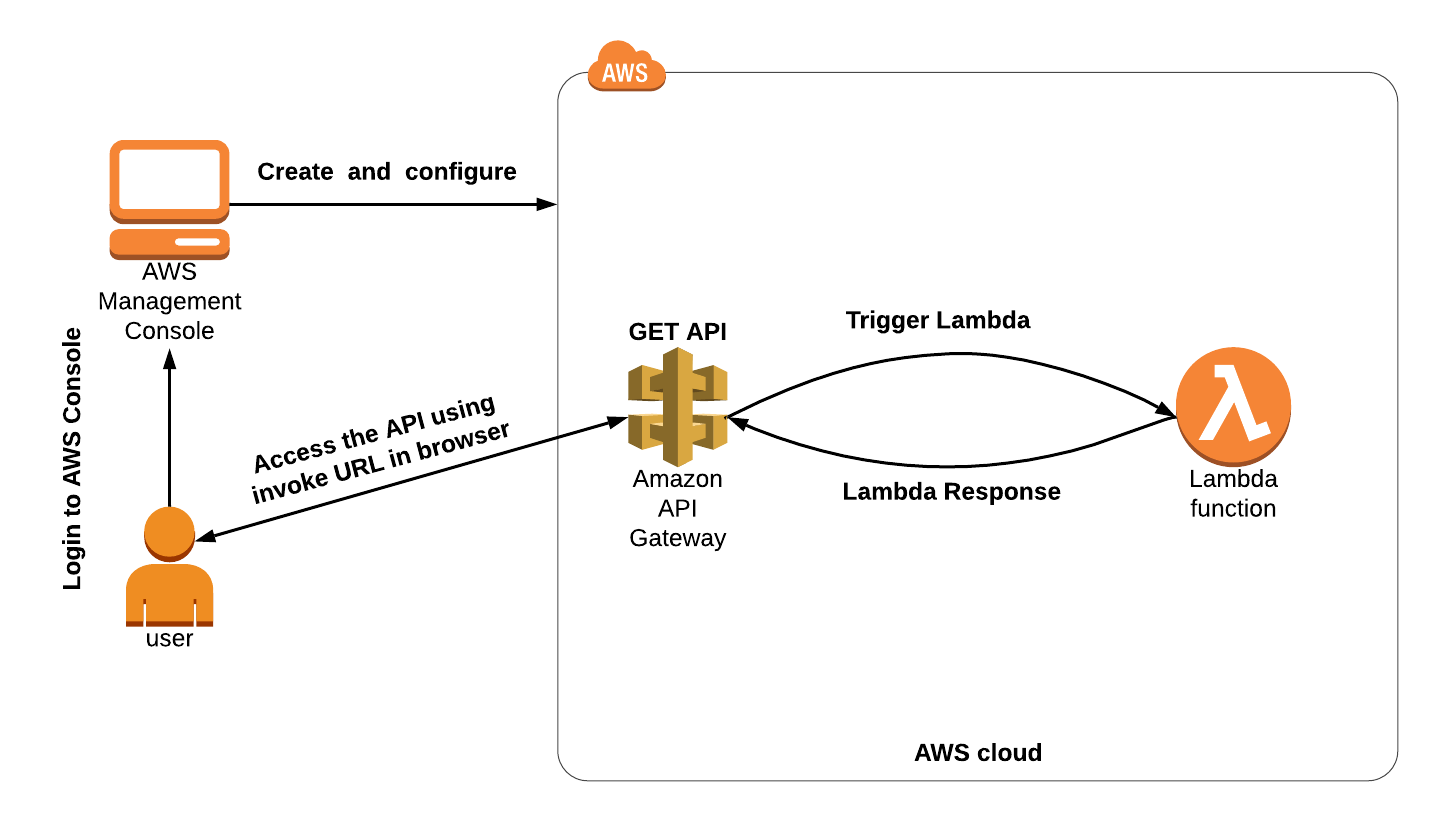
Building a Serverless Web Application with AWS Lambda and API Gateway Now that we have a basic understanding of serverless computing, AWS Lambda, and API Gateway, let's dive into building a serverless web application.
Step 1: Design your application architecture
The first step in building a serverless web application is to design your application architecture. This involves identifying the components of your application, such as the user interface, data storage, and API endpoints.
Step 2: Create AWS Lambda functions
The next step is to create AWS Lambda functions that will handle the logic of your application. AWS Lambda functions can be created using the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or a serverless framework such as Serverless or AWS SAM.
Step 3: Create API endpoints using API Gateway
Once your AWS Lambda functions are created, you can create API endpoints using API Gateway. API Gateway provides a web-based interface for creating, publishing, and managing RESTful APIs. You can use API Gateway to create API methods that map to your Lambda functions, define request and response models, and configure authentication and authorization.
Step 4: Deploy your application
After you have created your AWS Lambda functions and API endpoints, you can deploy your application to AWS. This involves creating a deployment package that includes your Lambda functions and API Gateway configuration and deploying it to AWS using the AWS Management Console or AWS CLI.
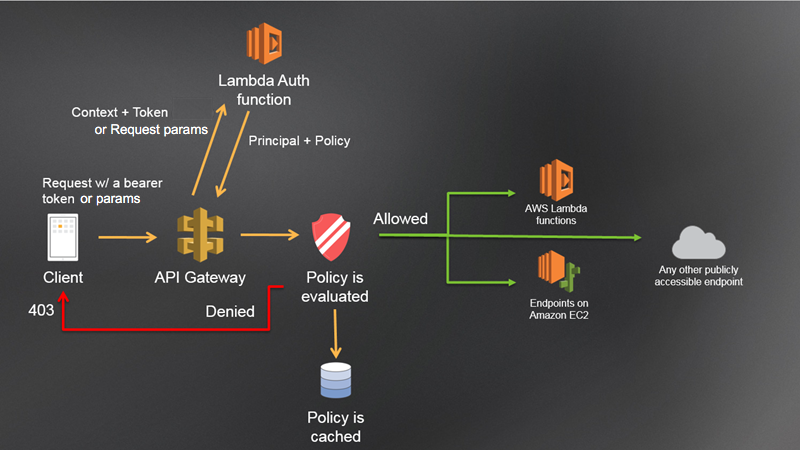
Best Practices for Serverless App Development
When developing serverless web applications with AWS Lambda and API Gateway, it is important to follow best practices to ensure that your application is scalable, efficient, and cost-effective. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
-
Use the right tool for the job: AWS Lambda and API Gateway are powerful tools, but they may not be the best fit for every use case. Make sure to choose the right tool for the job.
-
Design for scalability: Design your application with scalability in mind. This includes using asynchronous programming, breaking your application into small, reusable functions, and using auto-scaling groups to handle traffic spikes.
-
Optimize for cost: Serverless computing can be cost-effective, but it's important to optimize your application for cost.
-
Use caching: Use caching to reduce the number of requests made to your application and improve performance. API Gateway supports caching, and you can also use services like Amazon ElastiCache or Amazon CloudFront to cache data.
-
Monitor and log: Serverless computing can make it more challenging to monitor and debug your application, so it's important to implement logging and monitoring. AWS CloudWatch can be used to monitor your Lambda functions and API Gateway, and you can also use third-party tools like New Relic or Datadog.
-
Secure your application: Security is important in any application, and serverless applications are no exception. Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your Lambda functions and API Gateway, and implement encryption to protect sensitive data.
Conclusion
Serverless computing has made it easier than ever for developers to build, deploy, and scale applications. AWS Lambda and API Gateway are two powerful tools that can be used to build serverless web applications. By following best practices and designing your application with scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in mind, you can build serverless applications that are highly performant and secure.
In conclusion, building a serverless web application with AWS Lambda and API Gateway is a great way to take advantage of the benefits of serverless computing. With these powerful tools, developers can focus on building great applications without the hassle of managing infrastructure or servers. By following best practices and designing your application with scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in mind, you can build highly performant and secure serverless applications that meet the needs of your users.
Click To Read On Global Platform - Medium
Read - How I got certified as AWS Developer Associate, Get Hands-On with AWS: Learn and Apply with these Practical Applications
Maa Brahmacharini is the second form of Goddess Durga in Hindu mythology. This form of the goddess is worshipped on the second day of Navratri, which is a nine-day festival that celebrates the victory of good over evil. The name 'Brahmacharini' is derived from two words, 'Brahma' and 'charini', which mean 'one who practices penance' and 'the one who goes on foot', respectively. Hence, Maa Brahmacharini is the goddess of penance, purity, and sacrifice.
The depiction of Maa Brahmacharini is that of a beautiful young woman dressed in white, holding a japa mala or prayer beads in her right hand and a kamandal or water utensil in her left hand. She is shown walking barefoot with a calm and composed expression on her face. Her attire represents purity, simplicity, and austerity, which are the virtues that she embodies.

The legend behind Maa Brahmacharini's form is that she was born to King Himalaya and Queen Maina. Her name was Parvati, and she was known for her beauty and grace. She fell in love with Lord Shiva and wanted to marry him. However, Lord Shiva was known for his asceticism and did not want to get married. Parvati was determined to win him over, so she left her luxurious life and went to the forest to do penance and practice austerities.
Parvati meditated for years, enduring extreme heat and cold and subsisting on a diet of fruits and roots. She became known as Brahmacharini, the one who practices celibacy and austerity. Her unwavering devotion and self-control impressed Lord Shiva, and he eventually agreed to marry her.
The significance of Maa Brahmacharini's form is that it teaches us the importance of self-discipline, sacrifice, and determination. She is an inspiration for those who want to achieve success in life through hard work and perseverance. Her form also teaches us the importance of renunciation of material desires and attaining spiritual knowledge.
During Navratri, Maa Brahmacharini is worshipped on the second day of the festival. Devotees offer flowers, fruits, and sweets to her and chant mantras in her honor. By worshipping Maa Brahmacharini, we seek her blessings for spiritual growth and the strength to overcome our material desires.
Maa Brahmacharini is believed to have meditated for years in the forests of the Himalayas, and her worship is said to grant spiritual enlightenment, self-control, and detachment from worldly desires. She is considered an embodiment of tapasya, or penance, which is the path to attaining self-realization and liberation. Her teachings emphasize the importance of discipline, restraint, and renunciation in the pursuit of spiritual goals.

The significance of Maa Brahmacharini's worship is not limited to spiritual enlightenment alone. It also has a broader social and cultural significance. Her worship teaches us to lead a simple and disciplined life, practice self-restraint, and work hard with dedication and perseverance. These values are essential for personal growth and also contribute to the betterment of society as a whole.
In conclusion, Maa Brahmacharini is an embodiment of the divine feminine energy that represents knowledge, wisdom, and determination. She is a symbol of purity, simplicity, and austerity, and her worship during Navratri is believed to bring blessings of spiritual growth, strength, and success. May we all seek her blessings and strive to embody her virtues in our daily lives.

Chaitra Navratri is a Hindu festival that is celebrated for nine days during the Hindu month of Chaitra, which usually falls in March or April. This festival is celebrated with great enthusiasm and devotion by Hindus all over the world, and it marks the beginning of the Hindu New Year.
Navratri means 'nine nights' in Sanskrit, and during this festival, devotees worship the nine forms of the goddess Durga, also known as Navadurga. The nine forms of Durga are Shailaputri, Brahmacharini, Chandraghanta, Kushmanda, Skandamata, Katyayani, Kalaratri, Mahagauri, and Siddhidatri. Each form of Durga represents a particular attribute or quality and is worshipped accordingly.

The first day of Navratri is known as Ghatasthapana, which marks the beginning of the nine-day festival. On this day, a pot filled with water is placed in the puja room and decorated with mango leaves and a coconut. This post is considered to be a symbol of the goddess Durga, and it is worshiped throughout the nine days of the festival.

The first three days of Chaitra Navratri are dedicated to Goddess Durga, who is worshipped as the embodiment of power and energy. The next three days are dedicated to Goddess Lakshmi, the goddess of wealth and prosperity. The last three days are dedicated to Goddess Saraswati, the Goddess of knowledge and wisdom.
During Navratri, devotees observe fasts, perform pujas, and offer prayers to the goddess Durga. Many people also choose to refrain from consuming alcohol and non-vegetarian food during this period. It is believed that by observing these rituals, devotees can attain spiritual purification and can receive blessings from the goddess.
Apart from its religious significance, Chaitra Navratri also holds cultural and social importance. People decorate their houses with flowers and lights, and women wear new clothes and jewelry. Many communities organize Garba and Dandiya Raas dances during Navratri, where people dance to the beat of traditional music and celebrate the festival with great zeal and enthusiasm.
On the eighth day of Navratri, which is known as Ashtami, young girls are worshiped as embodiments of the goddess Durga. This day is also known as "Kanya Pujan," and it is believed that by worshiping young girls, one can receive the blessings of the goddess Durga.
On the ninth day of Chaitra Navratri, devotees worship the ninth form of Goddess Durga, known as Siddhidatri. The word "Siddhi" means "perfection" or "success," and "Datri" means "the giver." Goddess Siddhidatri is believed to be the ultimate giver of boons and blessings. She is also known as Adi Shakti, the original power or energy that created the universe.
The ninth and final day of Navratri is known as Navami, and it is considered to be the most important day of the festival. On this day, devotees offer prayers to the goddess Durga and seek her blessings. The festival culminates with the immersion of the pot, which is a symbol of the goddess Durga.
In conclusion, Chaitra Navratri is a festival that is celebrated with great devotion and enthusiasm by Hindus all over the world. It is a time to seek the blessings of the goddess Durga and to attain spiritual purification through fasting, prayer, and other rituals. This festival is a reminder of the power of the goddess, and of the importance of devotion and faith in our lives.

Cloud computing has become a game-changer in the tech industry, allowing businesses and individuals to leverage the power of the cloud to build, deploy, and manage applications and services at scale. Among the leading cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out as the most comprehensive and flexible platform, offering a vast array of services and tools to meet diverse needs and use cases.
In this blog, we'll explore 5 practical applications that will help you get hands-on with AWS and boost your cloud computing skills. Whether you're a developer, a system administrator, or a business owner, these applications will give you a taste of what AWS can do and how you can leverage it to build better, faster, and more secure applications.
1. Host a Static Website on Amazon S3
If you have a static website, you can use Amazon S3 to host it. To do this, you can follow these steps:
- Create an S3 bucket with a unique name.
- Enable static website hosting for your bucket.
- Upload your website files to your bucket.
- Configure your bucket policy to allow public access to your files.
- Optionally, use Amazon CloudFront to improve the performance and security of your website.

2. Build a Serverless Web Application with AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway
If you want to build a serverless web application, you can use AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway. To do this, you can follow these steps:
- Create a Lambda function that handles your application logic.
- Create an API Gateway REST API that exposes your Lambda function as an HTTP endpoint.
- Test your API using the API Gateway console or a REST client.
- Optionally, add authentication and authorization to your API using Amazon Cognito or AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Deploy your API to a stage and monitor its usage using Amazon CloudWatch.
Read Serverless App Development with AWS Lambda and API Gateway

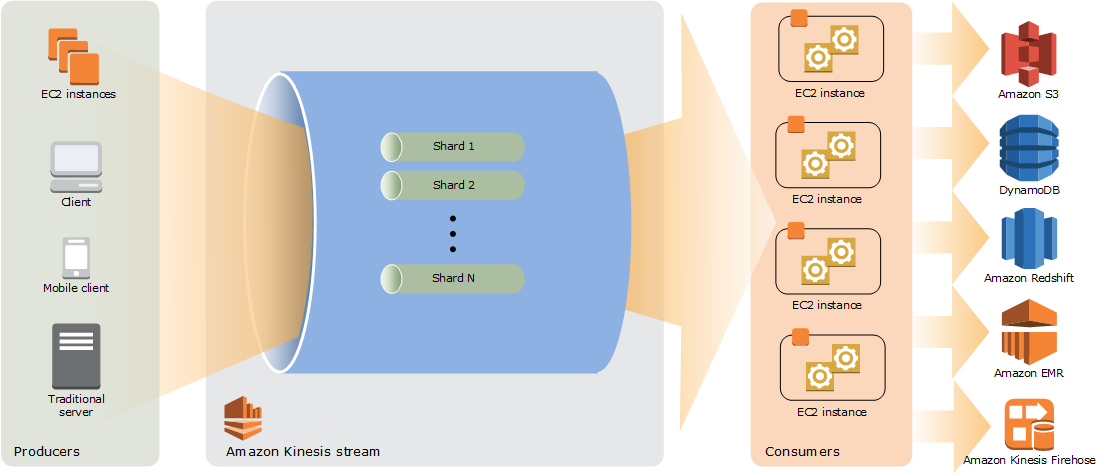
3. Process Data in Real-Time with Amazon Kinesis
If you want to process data in real time, you can use Amazon Kinesis. To do this, you can follow these steps:
- Create a Kinesis data stream that receives your data.
- Create a Kinesis data analytics application that processes your data using SQL queries.
- Optionally, create a Kinesis data firehose delivery stream that stores your processed data in Amazon S3 or other destinations.
- Test your application using sample data or a data generator.
- Scale your application and monitor its performance using Amazon CloudWatch.
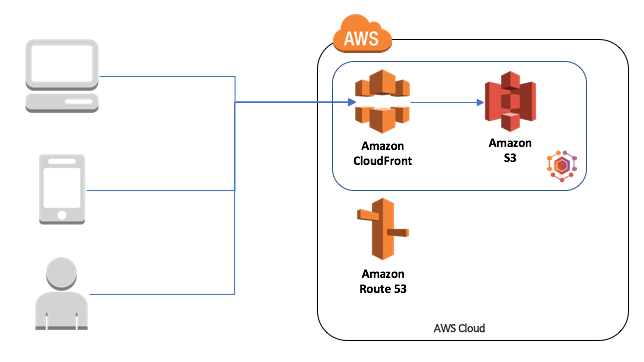
4. Create a Multi-Region Deployment with Amazon Route 53 and Amazon S3
If you want to create a multi-region deployment, you can use Amazon Route 53 and Amazon S3. To do this, you can follow these steps:
- Create an S3 bucket in each region that hosts your content or application.
- Enable static website hosting for each bucket.
- Create a Route 53 DNS record set that maps your domain name to your S3 buckets using latency-based routing.
- Test your deployment using a DNS lookup tool or a web browser.
- Optionally, use Amazon CloudFront to improve the performance and security of your deployment.
5. Build a Data Warehouse with Amazon Redshift
If you want to build a data warehouse, you can use Amazon Redshift. To do this, you can follow these steps:
- Create a Redshift cluster that stores your data.
- Load your data into your cluster using COPY or other methods.
- Create tables and views that organize and transform your data using SQL queries.
- Connect to your cluster using a SQL client or a BI tool.
- Monitor and optimize your cluster using Amazon Redshift console or Amazon CloudWatch.
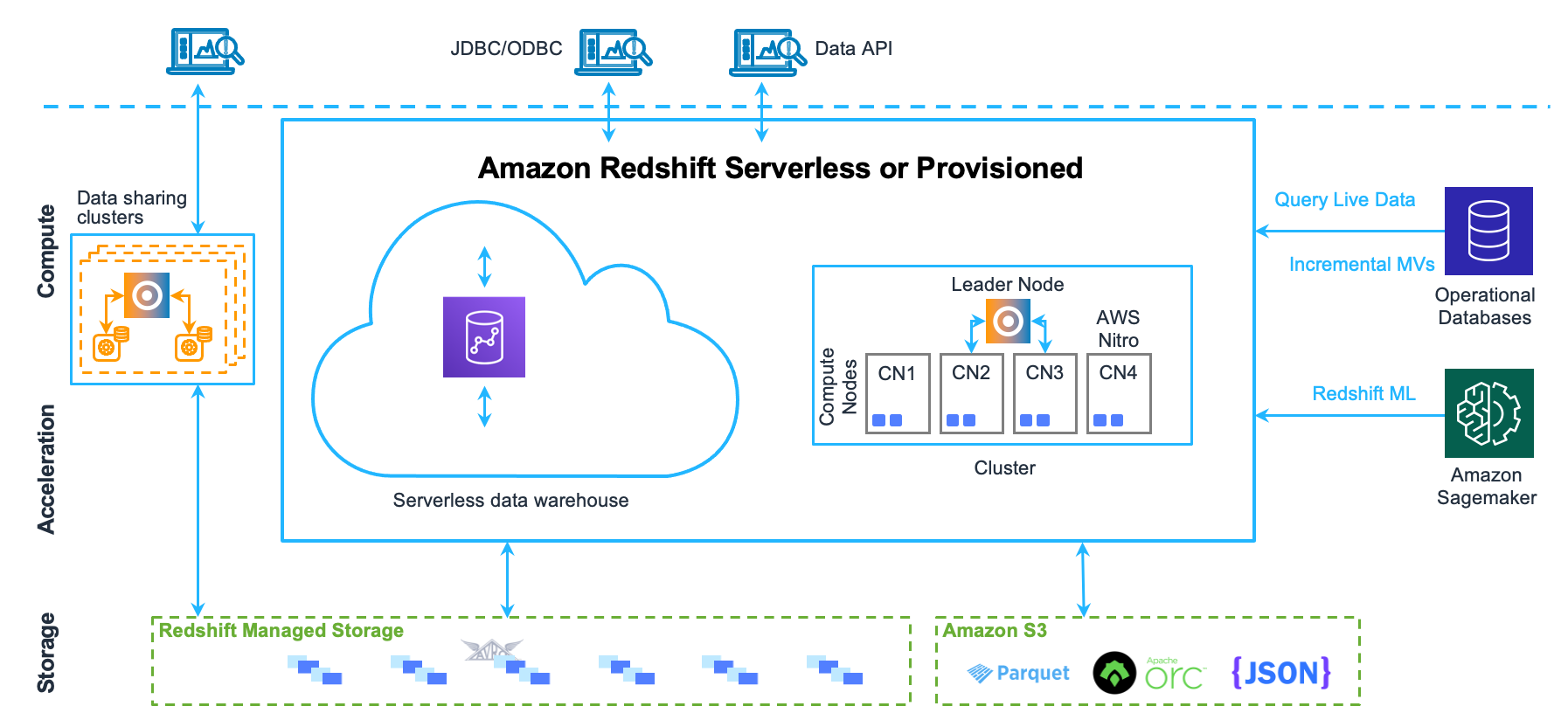
These are just a few examples of practical AWS applications using different AWS services. With AWS, the possibilities are endless and you can build and deploy a wide range of applications and services to meet your specific needs.

There are several popular customer review sites where businesses can collect customer reviews. Here are some of the most widely used platforms:
1. Google My Business: This platform allows businesses to manage their online presence across Google's search engine and maps. Customers can leave reviews and ratings on a business's Google My Business page, which can help boost visibility and credibility.
Benefits of Google My Business:
- Google is the world's largest search engine and controls over 90% of the search engine market share.
- Google can localize your review search, meaning it will only show results for businesses located in the area that you searched.
- It's free to create and customize your Google Business Profile. Setting up only takes a few minutes.
- Nearly 10% of Google's search algorithm is influenced by Google Reviews. The more positive reviews you have, the higher your business will rank on SERPs.
2. Yelp: Yelp is a popular review site for businesses, particularly in the restaurant and hospitality industries. Customers can leave reviews and ratings on a business's Yelp page, and businesses can respond to customer feedback.
Benefits of Yelp:
- Yelp has roughly 183 million monthly users worldwide.
- Anyone can sign up for Yelp and it's fairly easy for customers to leave a review — making it a good source of customer feedback.
- Yelp users are a tight-knit community. Active users will provide a lot of detailed feedback for your business.
- Research shows an increase of one star in your Yelp rating can increase revenue by 5-9%.
3. Amazon: Amazon is a popular e-commerce platform that allows customers to leave reviews and ratings for products sold on the site. Businesses can also create a storefront on Amazon to sell their products and collect customer feedback.
Benefits of Amazon Customer Reviews:
- Amazon has over 300 million users who can see your review.
- Amazon's rating system is straightforward and easy to understand.
- Amazon offers a product ranking feature that rates your product's popularity.
- Amazon users are loyal — 22% won't look at competitors if they discovered the product on Amazon.
4. TripAdvisor: TripAdvisor is a popular review site for the travel and tourism industry. Customers can leave reviews and ratings for hotels, restaurants, and attractions, and businesses can respond to customer feedback.
Benefits of TripAdvisor:
- TripAdvisor has collected over 887 million reviews for eight million companies.
- TripAdvisor Plus gives you access to discount hotel pricing for over 100,000 locations.
- The average TripAdvisor Plus member saves about $350 the first time they use their membership.
- TripAdvisor Business Advantage showcases your company's best reviews so customers see them first when reviewing your profile.
5. Facebook: Facebook allows businesses to create a page and collect reviews and ratings from customers. Facebook also offers advertising options to help businesses reach a wider audience.
Benefits of Facebook Ratings & Reviews:
- There are more than 2.7 billion users who are active on Facebook each month.
- To collect reviews on Facebook, all you need to do is set up a Facebook Business Profile.
- 2/3 of Facebook users visit a local business's Facebook Profile at least once a week.
- Facebook is a platform designed for communication. This increases the chance of having productive conversations with those who leave a review for your business.
Businesses must actively monitor and respond to customer reviews on these platforms to demonstrate that they value feedback and are committed to providing a positive customer experience. Responding to negative reviews constructively and respectfully can also help to mitigate any negative impact on a business's reputation and demonstrate a commitment to addressing customer concerns.
In conclusion, while customer review sites did not exist in the past, people still shared their opinions and experiences with products and services in different ways. Today, online review sites have become an important tool for businesses to collect feedback and improve customer experiences.

Serverless computing has revolutionized the way developers build, deploy, and scale applications. With serverless computing, developers no longer need to manage servers, infrastructure, or the operating system. Instead, they can focus on writing code and building applications that are scalable, efficient, and cost-effective.
AWS Lambda and API Gateway are two of the most popular serverless computing services provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). In this blog, we will discuss the basics of serverless computing, AWS Lambda, and API Gateway, and how to use them to build a serverless web application.
Basics of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider manages the infrastructure and automatically allocates computing resources as needed. The key benefits of serverless computing are scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Lambda functions can be used to process data, respond to events, and more. AWS Lambda supports a wide range of programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, Go, and Ruby.
API Gateway
AWS API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, and manage RESTful APIs. It integrates with AWS Lambda, allowing developers to create serverless APIs that can be used to build scalable web applications. API Gateway provides features such as authentication, authorization, and rate limiting, making it a powerful tool for building secure and efficient APIs.

Building a Serverless Web Application with AWS Lambda and API Gateway Now that we have a basic understanding of serverless computing, AWS Lambda, and API Gateway, let's dive into building a serverless web application.
Step 1: Design your application architecture
The first step in building a serverless web application is to design your application architecture. This involves identifying the components of your application, such as the user interface, data storage, and API endpoints.
Step 2: Create AWS Lambda functions
The next step is to create AWS Lambda functions that will handle the logic of your application. AWS Lambda functions can be created using the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or a serverless framework such as Serverless or AWS SAM.
Step 3: Create API endpoints using API Gateway
Once your AWS Lambda functions are created, you can create API endpoints using API Gateway. API Gateway provides a web-based interface for creating, publishing, and managing RESTful APIs. You can use API Gateway to create API methods that map to your Lambda functions, define request and response models, and configure authentication and authorization.
Step 4: Deploy your application
After you have created your AWS Lambda functions and API endpoints, you can deploy your application to AWS. This involves creating a deployment package that includes your Lambda functions and API Gateway configuration and deploying it to AWS using the AWS Management Console or AWS CLI.

Best Practices for Serverless App Development
When developing serverless web applications with AWS Lambda and API Gateway, it is important to follow best practices to ensure that your application is scalable, efficient, and cost-effective. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
-
Use the right tool for the job: AWS Lambda and API Gateway are powerful tools, but they may not be the best fit for every use case. Make sure to choose the right tool for the job.
-
Design for scalability: Design your application with scalability in mind. This includes using asynchronous programming, breaking your application into small, reusable functions, and using auto-scaling groups to handle traffic spikes.
-
Optimize for cost: Serverless computing can be cost-effective, but it's important to optimize your application for cost.
-
Use caching: Use caching to reduce the number of requests made to your application and improve performance. API Gateway supports caching, and you can also use services like Amazon ElastiCache or Amazon CloudFront to cache data.
-
Monitor and log: Serverless computing can make it more challenging to monitor and debug your application, so it's important to implement logging and monitoring. AWS CloudWatch can be used to monitor your Lambda functions and API Gateway, and you can also use third-party tools like New Relic or Datadog.
-
Secure your application: Security is important in any application, and serverless applications are no exception. Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your Lambda functions and API Gateway, and implement encryption to protect sensitive data.
Conclusion
Serverless computing has made it easier than ever for developers to build, deploy, and scale applications. AWS Lambda and API Gateway are two powerful tools that can be used to build serverless web applications. By following best practices and designing your application with scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in mind, you can build serverless applications that are highly performant and secure.
In conclusion, building a serverless web application with AWS Lambda and API Gateway is a great way to take advantage of the benefits of serverless computing. With these powerful tools, developers can focus on building great applications without the hassle of managing infrastructure or servers. By following best practices and designing your application with scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in mind, you can build highly performant and secure serverless applications that meet the needs of your users.
Click To Read On Global Platform - Medium
Read - How I got certified as AWS Developer Associate, Get Hands-On with AWS: Learn and Apply with these Practical Applications





